More and more people suffer from depression. The severity and symptoms are wide-ranging. Children and adolescents are also more frequently affected nowadays. Anyone who feels depressed or powerless over a longer period of time and can rule out physical causes – such as vitamin D3 deficiency – can be helped by antidepressants after consulting a doctor. The most important thing here is the regularity of intake.
In the case of physical complaints, it is usually enough to prescribe the appropriate medication. In the case of psychological problems, on the other hand, the path to the right medication can be a long one. This is because our brain is extremely complex and by no means as well researched as the human body.
Also, not all people have good experiences with antidepressants. Possible side effects, such as high blood pressure, stomach problems or headaches, can be perceived as so burdensome that the antidepressants are soon discontinued. In addition, many patients are also concerned that this type of drug can quickly become addictive. Once the right antidepressant has been found, however, the quality of life can improve abruptly and sustainably.
What are antidepressants and how do they work?
Antidepressants are psychotropic drugs – the term used to describe medications used to treat mental illness. It is important to know that antidepressants are neither stimulant nor soporific, nor can they be addictive. If you are in a depressive phase, some processes in the brain do not take place as they should.
The chemical substances in the brain, that mediate the communication between the nerve cells of your grey matter, no longer work at the usual level. This is where antidepressants come in and try to remedy the resulting dysfunctions and channel more messenger substances into the synaptic cleft. This area – the space between two communicating nerve cells – is important for the transmission of nerve impulses.
Antidepressants strengthen the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine and dopamine. As a result, the nerve cells can communicate better with each other again. However, it can take several days to weeks before the depressive symptoms become less pronounced and a feeling of improvement sets in.
These antidepressants are commonly used:
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which include, for example, the drugs fluvoxamine, fluoxetine, citalopram and sertraline
- Selective serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), which include, for example, duloxetine and venlafaxine
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), examples of which are amitryptiline and clomipramine.

Treat depression in the long term
If you have found the right medication and feel better, you should not stop taking antidepressants immediately. While this may seem tempting, it can soon lead to plunging into the next depressive phase. It is recommended that treatment be continued for up to six months after recovery, after which the drug can be carefully phased out. This means taking smaller and smaller doses of it until you eventually drop it altogether.
The following therapeutic measures can support drug treatment:
- Light therapy: the daily “light shower” increases the serotonin level
- Exercise therapy: all types of exercise can help strengthen mental health
- Healthy diet: omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated fatty acids are important for the formation of neurotransmitters
Of course, these measures do not replace antidepressants, but they can support the body in the recovery process.
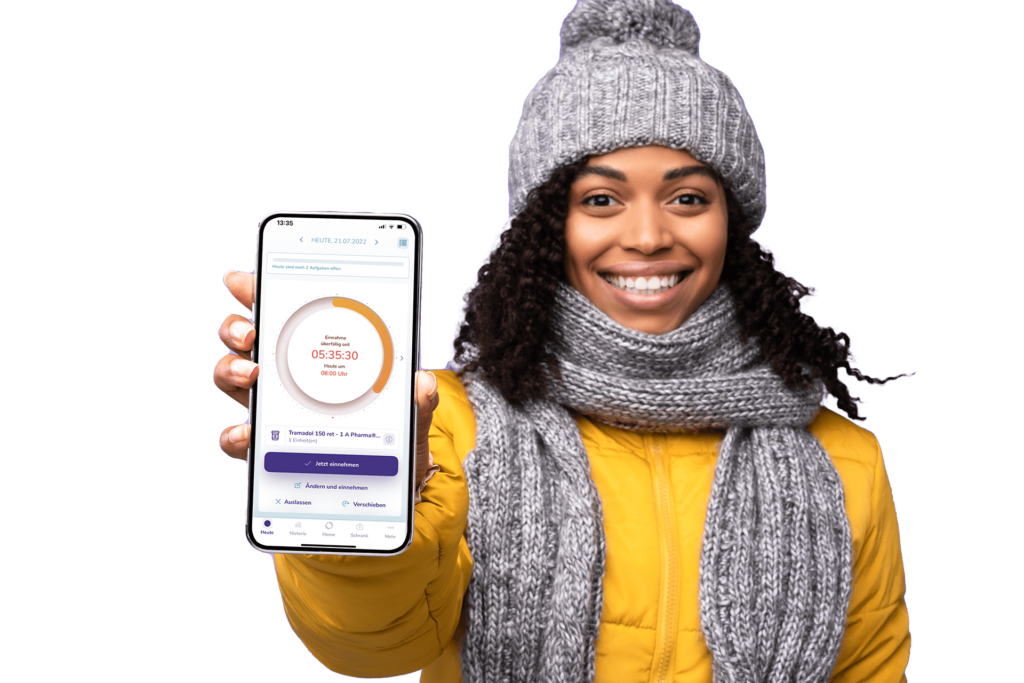
Taking antidepressants regularly: the TOM app helps
Especially in the case of antidepressants, it is essential to take them regularly. Are you a bit forgetful and don’t always remember to take your pills? The TOM app reliably reminds you to take your medication every day. A new drug is added and another is dropped? No problem! In the app’s virtual medicine cabinet, you can reorder your medications at any time. Download the TOM APP now and never forget to take your antidepressants again.